T-Cells and TA-GVHD
T-Cells and Transfusion-Associated Graft Versus Host Disease (TA-GVHD)
Reducing the Risk of TA-GVHD
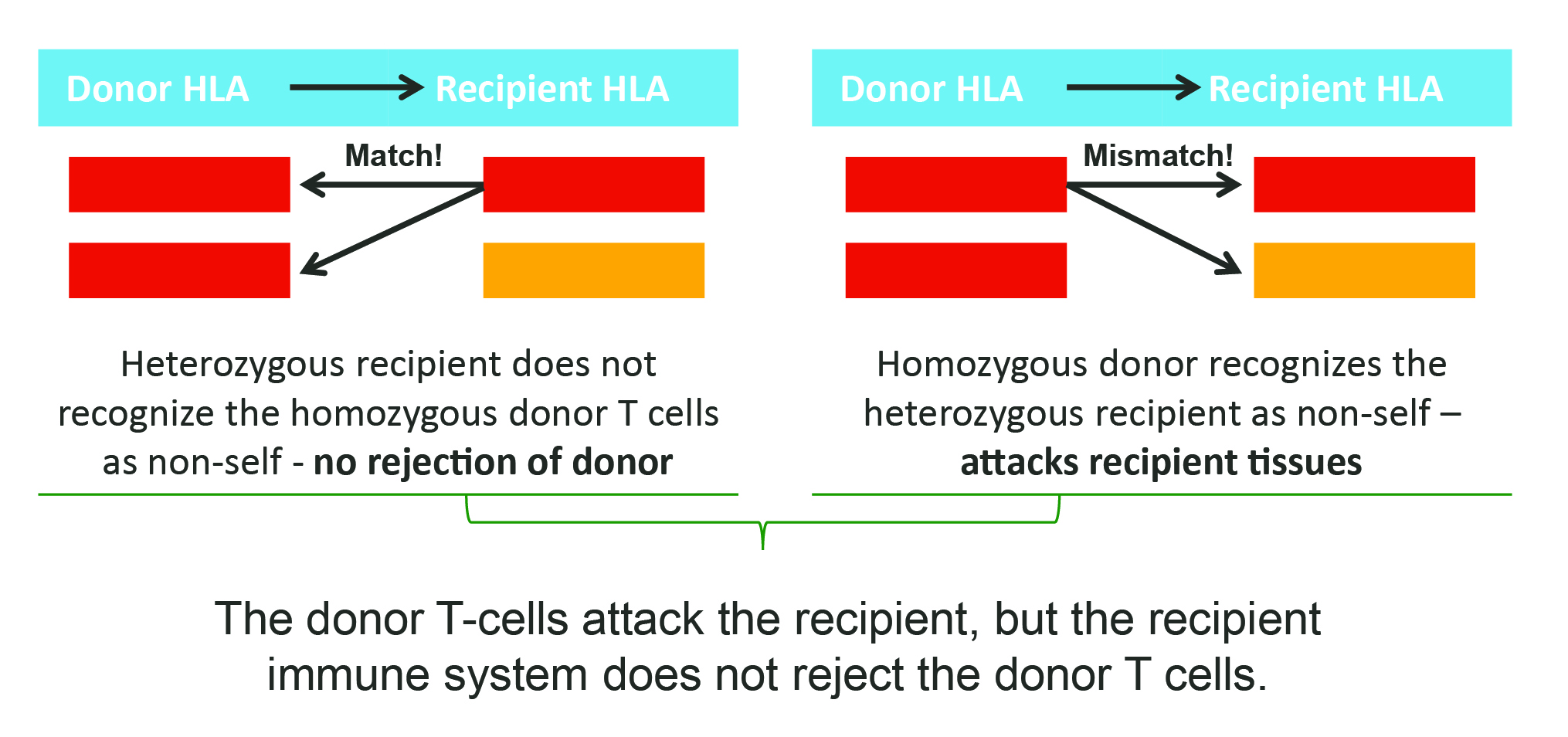
Transfusion-Associated Graft-versus-Host Disease (TA-GVHD) is a rare complication in which viable T-cells from the donor engraft and subsequently attack the recipient’s cells. TA-GVHD is generally thought to occur only in immunocompromised patients, but there are cases reported in immunocompetent individuals.1,2
Ability to reduce the risk of TA-GVHD is based on halting T-cell replication either by:
- Leukofiltration (considered ineffective based on case reports of TA-GVHD with leukoreduced products)3
- Contaminating T-cell reduction
- Irradiation4
- INTERCEPT treatment6
Irradiation has been approved for many years as a means to reduce TA-GVHD risk. However, T-cell activity studies have shown that gamma irradiation only partially inhibits markers of activity, mainly cytokine accumulation. In the same study, pathogen reduction eliminated this cytokine accumulation.5
Figure: Comparison between gamma irradiation and psoralen/UVA treatment.6,7

FDA and AABB Standard 5.19.4.1 accept INTERCEPT as an alternative to gamma irradiation for the prevention of TA-GVHD*.8,9
AABB Standards for Prevention of TA-GVHD
AABB standard 5.19.4.1 cites the “acceptable methods known to prevent transfusion-associated graft-vs-host disease include irradiation and pathogen reduction technology known to inactivate residual leukocytes that is cleared or approved by the FDA or Competent Authority.”8
1. McMilin, K. and R. Johnson, HLA homozygosity and the risk of related-donor transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease. Transfus Med Rev, 1993. 7(1): p. 37-41. 2. Thaler , M., et al., The Role of Blood from HLA-Homozygous Donors in Fatal Transfusion-Associated Graft-versus-Host Disease after Open-Heart Surgery. New England Journal of Medicine, 1989. 321(1): p. 25-28. 3. Kopolovic, I., et al., A systematic review of transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease. Blood, 2015. 126(3): p. 406-14. 4. AABB. Circular of Information for the Use of Human Blood and Blood Components. Bethesda, MD: AABB; 2017. 5. Hei, D.J., et al., Elimination of cytokine production in stored platelet concentrate aliquots by photochemical treatment with psoralen plus ultraviolet A light. Transfusion, 1999. 39(3): p. 239-48. 6. Grass JA, Hei DJ, Metchette K, et al. Inactivation of leukocytes in platelet concentrates by photochemical treatment with psoralen plus UVA. Blood 1998;91:2180-8. 7. Setlow R, Setlow J. Effects of radiation on polynucleotides. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng 1972;1:293-346. 8. The INTERCEPT Blood System for Platelets Package Insert, Cerus Corporation. 9. “Standards for Blood Banks and Transfusion Services,” AABB, 33rd edition, 2022.